 Bacteroids in a soybean root nodule.
Bacteroids in a soybean root nodule.
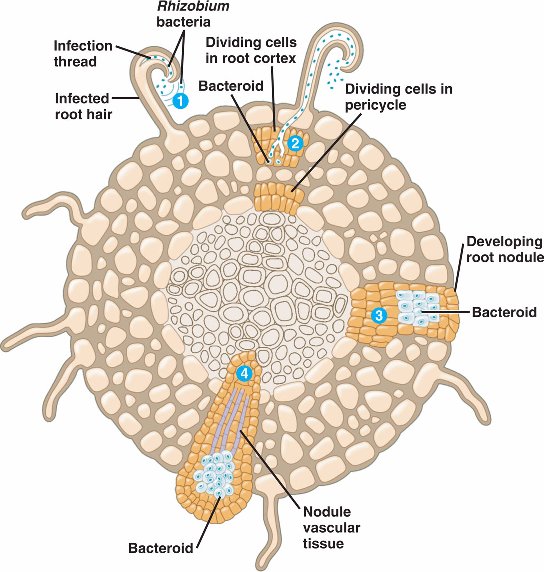
- Root hairs form an infection thread by invagination of the plasma membrane.
- Rhizobium bacteria penetrate the infection thread, and form bacteroids within vesicles.
- Root cells grow around a bacteroid, forming a nodule.
- The nodule develops vascular tissue that facilitate exchange of materials between bacteria and plant.
 Bacteroids in a soybean root nodule.
Bacteroids in a soybean root nodule.